Project Background
With the advancement of Internet of Things (IoT) technology, wireless sensing and wireless data transmission applications are becoming increasingly widespread. Utilizing micro-power networking technology to construct an advanced grid information architecture is also a major application direction in current power automation. However, due to power limitations in the ISM frequency bands, transmission distance is constrained; using purely wireless networking in high-rise buildings presents the following challenges:
- Latency in multi-hop networking,
- Signal dead zones,
- Node energy efficiency.
To better address the above reasons and the transmission difficulties encountered by actual customers in practical use, a hybrid networking approach based on our company's proprietary wired networking bus, LZBUS, combining "wired + wireless" is proposed.
LZBUS Overview
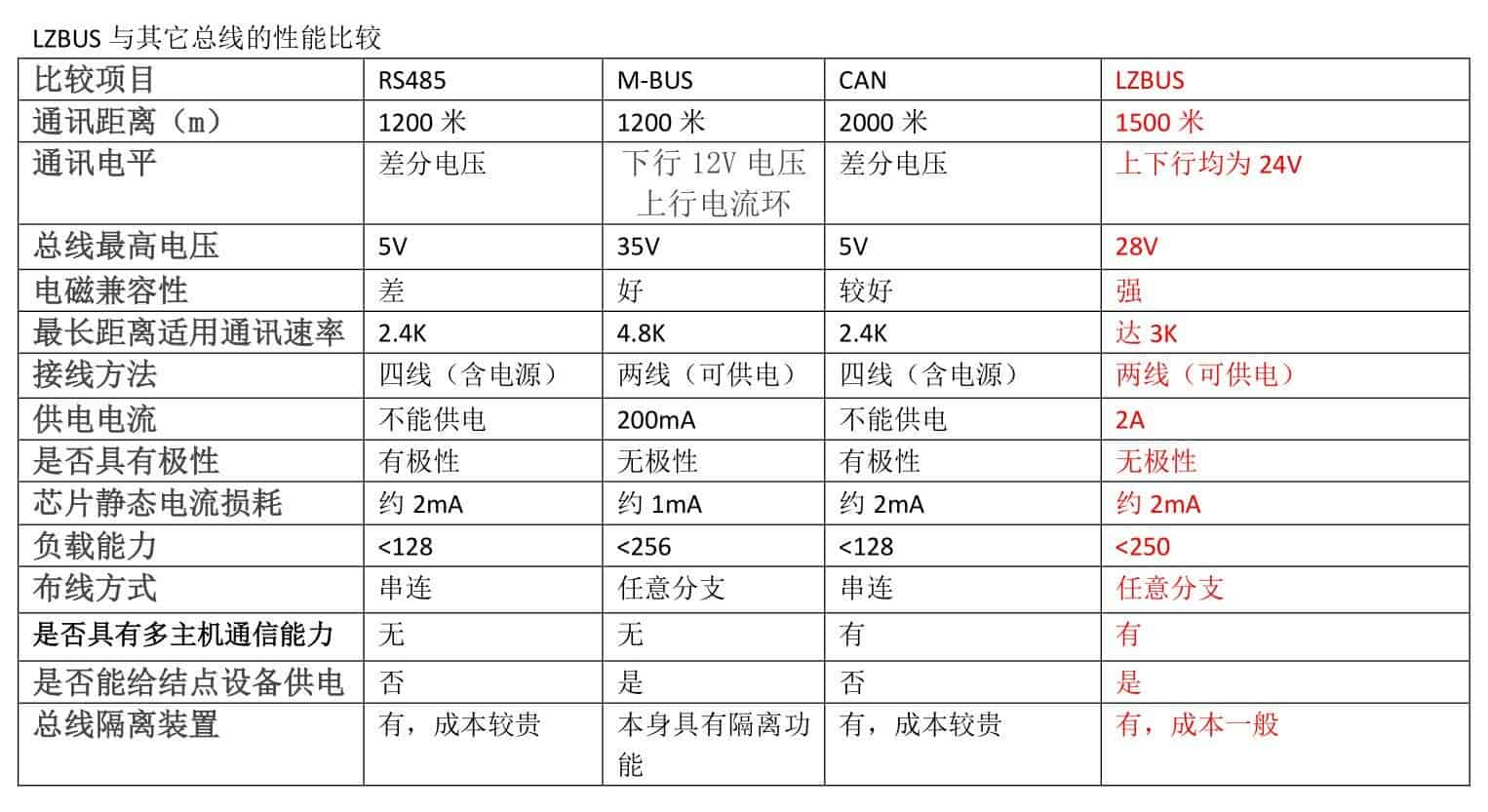
The LZBUS single bus is a long-distance, one-master-multiple-slaves, single-wire transmission bus. A system communicating via the LZBUS bus can be referred to as an LZBUS system. An LZBUS system consists of one master and several nodes. The communication distance varies with cable thickness; a 1 mm² cable can achieve a communication distance of over 1500 meters.
The external wiring for the LZBUS single bus includes a power line (VBUS), a signal line (S), and a ground line (GND). When the system bus load current is relatively low (<2A), nodes can draw power from the bus, meaning communication requires only two wires (GND, S). Furthermore, nodes can be configured for non-polarized communication using a bridge rectifier, meaning the S and GND lines do not require specific polarity.
If the system load current is high, a three-wire system can be used, allowing the entire system's load current to exceed 10A. This eliminates the need for individual power supply for each node, facilitating engineering cabling.
The system schematic is as follows:
The LZBUS system operates in a one-master-multiple-slaves manner, with the master polling the nodes to collect data from each node or control the digital output of the nodes. During data acquisition, a single frame of instructions from the LZBUS master can collect data from up to 16 nodes with consecutive logical addresses. However, when using a two-wire communication system, it is recommended to collect data from a maximum of 4 nodes with consecutive logical addresses at a time.
Data Transmission Networking Solution Based on Wired Bus LZBUS + Wireless
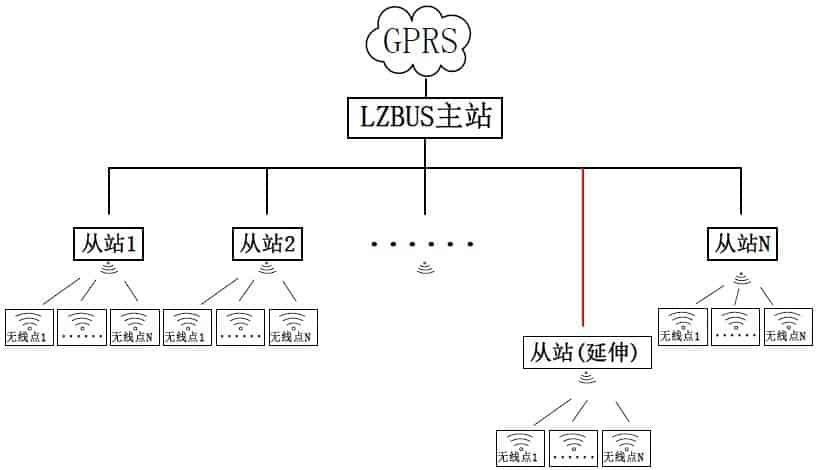
Solution Diagram

Solution Implementation Principle
The entire system consists of GPRS, the LZBUS bus (including master and slave stations), and wireless nodes.
LZBUS communicates with GPRS via a serial port. The master station communicates with each slave station via two wires. Each slave station is connected to a wireless data transmission module, which communicates with the wireless nodes under its jurisdiction. Each slave station can communicate with its managed wireless nodes through address identification.
If there is a communication overlap area between wireless nodes managed by two adjacent slave stations, wireless nodes in different slave station areas can be set to operate on different frequencies. This way, even if adjacent slave stations simultaneously query their managed modules, wireless conflicts will not occur.
Content Reviewer:
 Professional IoT solution equipment supplier
Professional IoT solution equipment supplier 


